Test for a difference in means of a single feature between clusters of observations identified via k-means clustering.
kmeans_inference_1f.RdThis function tests the null hypothesis of no difference in the means of a given
feature between a pair of clusters obtained via k-means clustering. The clusters
are numbered as per the results of the kmeans_estimation function in the CADET package.
By default, this function assumes that the features are independent. If known,
the variance of feature feat (\(\sigma\)) can be passed in using the
sigma argument; otherwise, an estimate of \(\sigma\) will be used.
kmeans_inference_1f(
X,
k,
cluster_1,
cluster_2,
feat,
iso = FALSE,
sig = NULL,
covMat = NULL,
iter.max = 10,
seed = 1234
)Arguments
- X
Numeric matrix; \(n\) by \(q\) matrix of observed data
- k
Integer; the number of clusters for k-means clustering
- cluster_1, cluster_2
Two different integers in 1,...,k; two estimated clusters to test, as indexed by the results of
kmeans_estimation.- feat
Integer selecting the feature to test.
- iso
Boolean. If
TRUE, an isotropic covariance matrix model is used. Default iscode.- sig
Numeric; noise standard deviation for the observed data, a non-negative number; relevant if
iso=TRUE. If it's not given as input, a median-based estimator will be by default (see Section 4.2 of our manuscript).- covMat
Numeric matrix; if
isois FALSE, *required* \(q\) by \(q\) matrix specifying \(\Sigma\).- iter.max
Positive integer; the maximum number of iterations allowed in k-means clustering algorithm. Default to
10.- seed
Random seed for the initialization in k-means clustering algorithm.
Value
Returns a list with the following elements:
p_naivethe naive p-value which ignores the fact that the clusters under consideration are estimated from the same data used for testingpvalthe selective p-value \(p_{kmeans,j}\) in Chen and Gao (2023+)final_intervalthe conditioning set of Chen and Gao (2023+), stored as anIntervalsclass object.test_stattest statistic: the (signed) difference in the empirical means of the specified feature between two estimated clusters.final_clusterEstimated clusters via k-means clustering.
Details
Setting iso to FALSE (default) allows the features to be dependent, i.e.
\(Cov(X_i) = \Sigma\). \(\Sigma\) need to be passed in using the covMat argument.
For better rendering of the equations, visit https://yiqunchen.github.io/CADET/reference/index.html.
Consider the generative model \(X ~ MN(\mu,I_n,\sigma^2 I_q)\). First recall that k-means clustering
solves the following optimization problem
$$ \sum_{k=1}^K \sum_{i \in C_k} \big\Vert x_i - \sum_{i \in C_k} x_i/|C_k| \big\Vert_2^2 , $$
where \(C_1,..., C_K\) forms a partition of the integers \(1,..., n\), and can be regarded as
the estimated clusters of the original observations. Lloyd's algorithm is an iterative apparoach to solve
this optimization problem.
Now suppose we want to test whether the means of two estimated clusters cluster_1 and cluster_2
are equal; or equivalently, the null hypothesis of the form \(H_{0,j}: (\mu^T \nu)_j = 0\) versus
\(H_{1,j}: (\mu^T \nu)_j \neq 0\) for suitably chosen \(\nu\) and feature number j.
This function computes the following p-value: $$P \Big( |(X^T\nu)_j| \ge |(x^T\nu)_j| \; | \; \bigcap_{t=1}^{T}\bigcap_{i=1}^{n} \{ c_i^{(t)}(X) = c_i^{(t)}( x ) \}, U(X) = U(x) \Big),$$ where \(c_i^{(t)}\) is the is the cluster to which the \(i\)th observation is assigned during the \(t\)th iteration of Lloyd's algorithm, and \(U\) is defined in Section 3.2 of Chen and Gao (2023+). The test that rejects \(H_{0,j}\) when this p-value is less than \(\alpha\) controls the selective Type I error rate at \(\alpha\), and has substantial power. Readers can refer to the Sections 2-4 in Chen and Gao (2023+) for more details.
References
Lloyd, S. P. (1957, 1982). Least squares quantization in PCM. Technical Note, Bell Laboratories. Published in 1982 in IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 28, 128–137.
Examples
library(CADET)
library(ggplot2)
set.seed(2022)
n <- 150
true_clusters <- c(rep(1, 50), rep(2, 50), rep(3, 50))
delta <- 10
q <- 2
mu <- rbind(c(delta/2,rep(0,q-1)),
c(rep(0,q-1), sqrt(3)*delta/2),
c(-delta/2,rep(0,q-1)) )
sig <- 1
# Generate a matrix normal sample
X <- matrix(rnorm(n*q, sd=sig), n, q) + mu[true_clusters, ]
# Visualize the data
ggplot(data.frame(X), aes(x=X1, y=X2)) +
geom_point(cex=2) + xlab("Feature 1") + ylab("Feature 2") +
theme_classic(base_size=18) + theme(legend.position="none") +
scale_colour_manual(values=c("dodgerblue3", "rosybrown", "orange")) +
theme(legend.title = element_blank(),
plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5))
 k <- 3
# Run k-means clustering with K=3
estimated_clusters <- kmeans_estimation(X, k,iter.max = 20,seed = 2023)$final_cluster
table(true_clusters,estimated_clusters)
#> estimated_clusters
#> true_clusters 1 2 3
#> 1 0 0 50
#> 2 0 50 0
#> 3 50 0 0
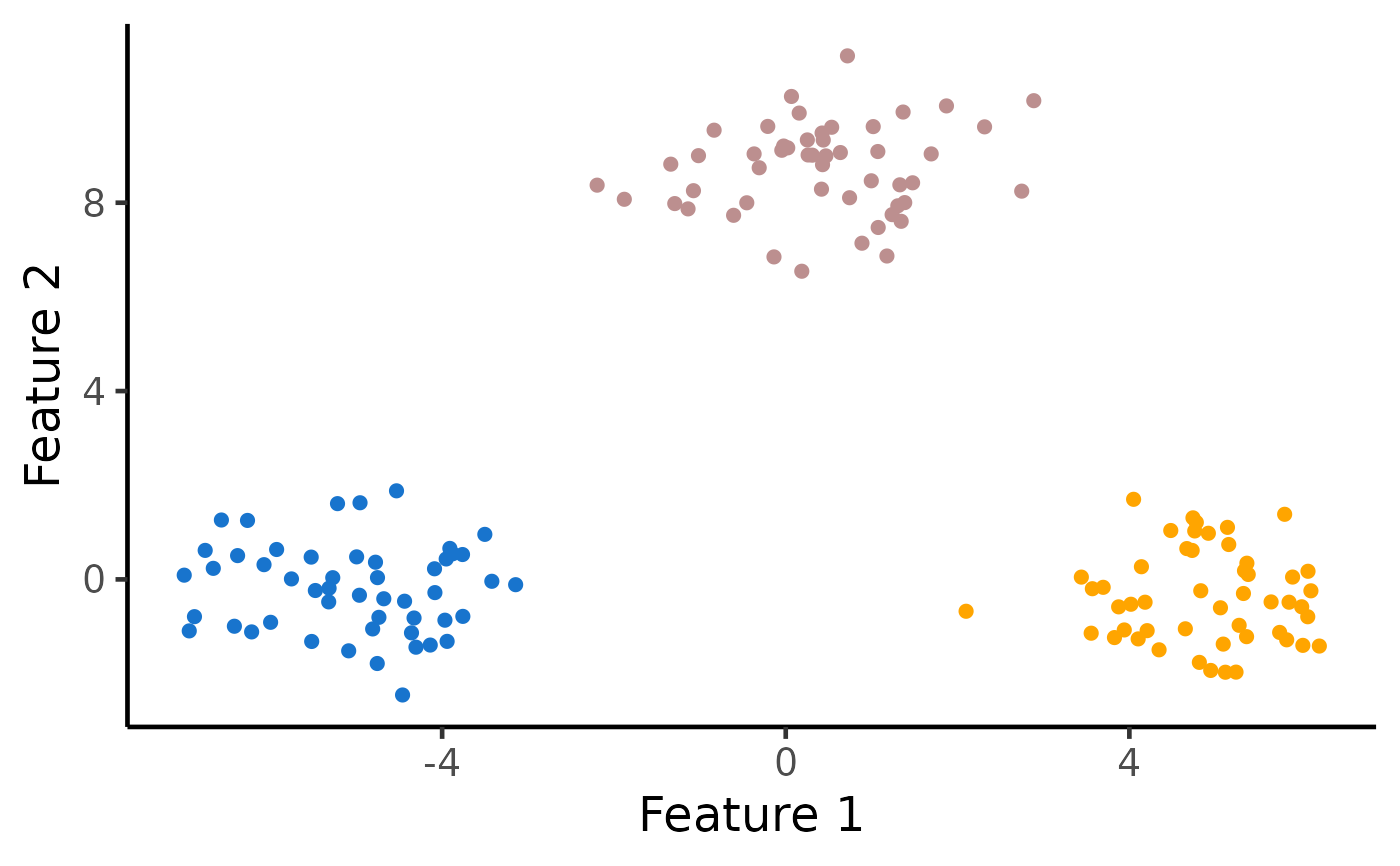
# Visualize the clusters
ggplot(data.frame(X), aes(x=X1, y=X2, col=as.factor(estimated_clusters))) +
geom_point(cex=2) + xlab("Feature 1") + ylab("Feature 2") +
theme_classic(base_size=18) + theme(legend.position="none") +
scale_colour_manual(values=c("dodgerblue3", "rosybrown", "orange")) +
theme(legend.title = element_blank(), plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5))
k <- 3
# Run k-means clustering with K=3
estimated_clusters <- kmeans_estimation(X, k,iter.max = 20,seed = 2023)$final_cluster
table(true_clusters,estimated_clusters)
#> estimated_clusters
#> true_clusters 1 2 3
#> 1 0 0 50
#> 2 0 50 0
#> 3 50 0 0
# Visualize the clusters
ggplot(data.frame(X), aes(x=X1, y=X2, col=as.factor(estimated_clusters))) +
geom_point(cex=2) + xlab("Feature 1") + ylab("Feature 2") +
theme_classic(base_size=18) + theme(legend.position="none") +
scale_colour_manual(values=c("dodgerblue3", "rosybrown", "orange")) +
theme(legend.title = element_blank(), plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5))
 # Let's test the difference between first feature across estimated clusters 1 and 2:
cl_1_2_feat_1 <- kmeans_inference_1f(X, k=3, 1, 2,
feat=1, iso=TRUE,
sig=sig,
covMat=NULL, seed=2023,
iter.max = 30)
cl_1_2_feat_1
#> $final_interval
#> Object of class Intervals_full
#> 1 interval over R:
#> (-5.45897268242358, -5.39453348487993)
#>
#> $final_cluster
#> [1] 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
#> [38] 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
#> [75] 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
#> [112] 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
#> [149] 1 1
#>
#> $test_stat
#> [1] -5.445953
#>
#> $cluster_1
#> [1] 1
#>
#> $cluster_2
#> [1] 2
#>
#> $feat
#> [1] 1
#>
#> $sig
#> [1] 1
#>
#> $covMat
#> NULL
#>
#> $scale_factor
#> [1] 0.04
#>
#> $p_naive
#> [1] 2.886169e-163
#>
#> $pval
#> [1] 0.0007753861
#>
#> $call
#> kmeans_inference_1f(X = X, k = 3, cluster_1 = 1, cluster_2 = 2,
#> feat = 1, iso = TRUE, sig = sig, covMat = NULL, iter.max = 30,
#> seed = 2023)
#>
#> attr(,"class")
#> [1] "kmeans_inference"
# Let's test the difference between first feature across estimated clusters 1 and 2:
cl_1_2_feat_1 <- kmeans_inference_1f(X, k=3, 1, 2,
feat=1, iso=TRUE,
sig=sig,
covMat=NULL, seed=2023,
iter.max = 30)
cl_1_2_feat_1
#> $final_interval
#> Object of class Intervals_full
#> 1 interval over R:
#> (-5.45897268242358, -5.39453348487993)
#>
#> $final_cluster
#> [1] 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
#> [38] 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
#> [75] 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
#> [112] 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
#> [149] 1 1
#>
#> $test_stat
#> [1] -5.445953
#>
#> $cluster_1
#> [1] 1
#>
#> $cluster_2
#> [1] 2
#>
#> $feat
#> [1] 1
#>
#> $sig
#> [1] 1
#>
#> $covMat
#> NULL
#>
#> $scale_factor
#> [1] 0.04
#>
#> $p_naive
#> [1] 2.886169e-163
#>
#> $pval
#> [1] 0.0007753861
#>
#> $call
#> kmeans_inference_1f(X = X, k = 3, cluster_1 = 1, cluster_2 = 2,
#> feat = 1, iso = TRUE, sig = sig, covMat = NULL, iter.max = 30,
#> seed = 2023)
#>
#> attr(,"class")
#> [1] "kmeans_inference"